Dismantling
The history of dismantling as a part of the decommissioning process starts from the moment when the decision on the immediate dismantling was adopted, i. e. dismantling should be commenced immediately after the suspension of the power plant.
 This method includes many advantages - complicated tasks that require special knowledge and skills will be performed by professionals of the enterprise who have worked with the equipment of the power plant for a long time. Some of the employees were even involved into the INPP construction and installation of the equipment works, therefore, their experience is of great importance for the safe decommissioning process.
This method includes many advantages - complicated tasks that require special knowledge and skills will be performed by professionals of the enterprise who have worked with the equipment of the power plant for a long time. Some of the employees were even involved into the INPP construction and installation of the equipment works, therefore, their experience is of great importance for the safe decommissioning process.
Even before the shutdown of the INPP the dismantling and decontamination of the equipment projects were prepared - B9 projects:
B-9/0 - INPP Building 117/1 Equipment Decontamination and Dismantling Project;
B-9/1 - INPP Unit 1 Turbine Hall Equipment Decontamination and Dismantling Project Development;
B-9/2 - INPP Building V1 Equipment Dismantling and Decontamination Design Development;
B-9/5 - INPP Boiler House Equipment Dismantling and Decontamination Design Development (119 building).
These projects are being prepared by consortiums of various international companies which have international experience in the field of decommissioning of nuclear objects. B9 projects encompass dismantling of only a part of power plant's equipment. Presently, the decision was taken to implement the rest of the equipment dismantling projects by the INPP professionals. Many design decisions taken earlier will be already tested in practice.
In 2009, one year before the closure of the Unit 2, the new structure of the INPP departments was prepared where the establishment of the Dismantling and Decontamination Service was envisaged. The departments which have all the necessary resources for dismantling process were included in this service.
The equipment that does not perform security functions and is not contaminated with radionuclides, i.e. does not require decontamination, is being dismantled first. Besides the main direct task for dismantling, the other tasks were raised in 2010:
- mastering of new technologies and equipment, accumulation of experience in the field of planning and work organization, improvement of professional skills of workers and specialists;
- preparation of facilities and buildings with decommissioned equipment for further operation;
- realization and reuse of the INPP dismantled equipment and materials;
- curtailment of maintenance and preservation expenses of decommissioned equipment and buildings;
- search of economically effective and safe equipment dismantling technologies.
Almost all departments of the power plant are being involved in the preparatory works which follow before dismantling of equipment:
- preparation of modifications and coordination with State Nuclear Power Safety Inspectorate (VATESI);
- sequestration of facilities - disconnection of water, steam, voltage sources, drainage, documentation handling;
- radiological characterization;
- preparation of detailed design;
- obtaining permission for the dissolution of fixed assets.
Sequence of starting unit dismantling
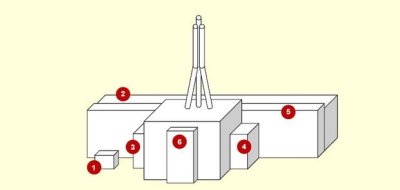 1. Emergency core cooling system water storage tanks (Building 117)
1. Emergency core cooling system water storage tanks (Building 117)
2. Turbine generators with auxiliary systems, feed facilities and heat supply facilities (Block G)
3. Reactor gas circuit and special venting system (Block V)
4. Low salt water and main coolant circuit bypass water treatment facilities (Block B)
5. Control room, electrical equipment and deaerators (Block D) heat pipe service/fire fighting (Unit 1 only)
6. Reactor building (Block A)

